MINERVA configuration: Administrator’s manual#
Administrator view#
Administrator view refers to the set of functionalities for web-based management of the content and configuration of your MINERVA instance.
Login#
Administrator view is accessible via the button with the lock icon in the upper left corner of the user view (see below). See also User manual - Main view).
![]() {:width=“400px”}
{:width=“400px”}
Many projects (maps, networks) can be hosted in parallel on a single MINERVA instance (see User manual - Accessing the project) and a user having administrator rights to at least one of them can log via ADMINISTRATOR link. After successful login, you will have access to the administrator panel to manage your MINERVA instance (see below).
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
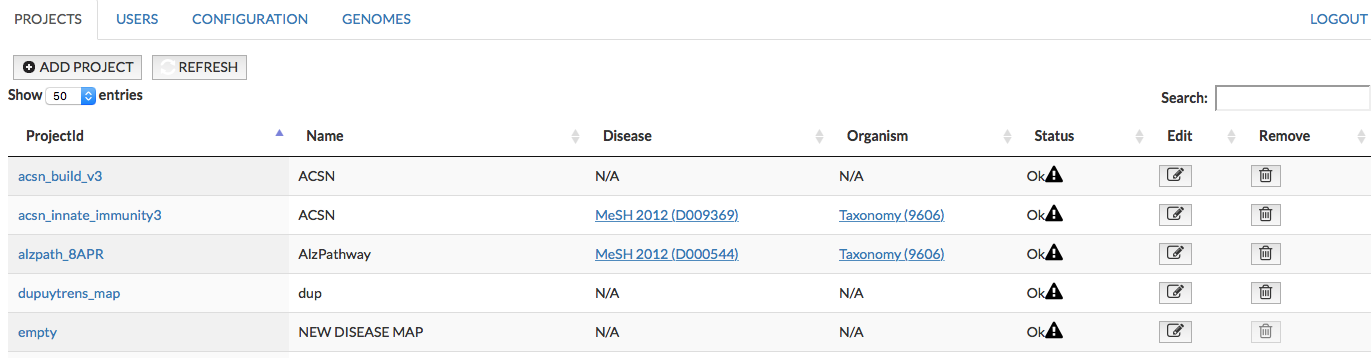
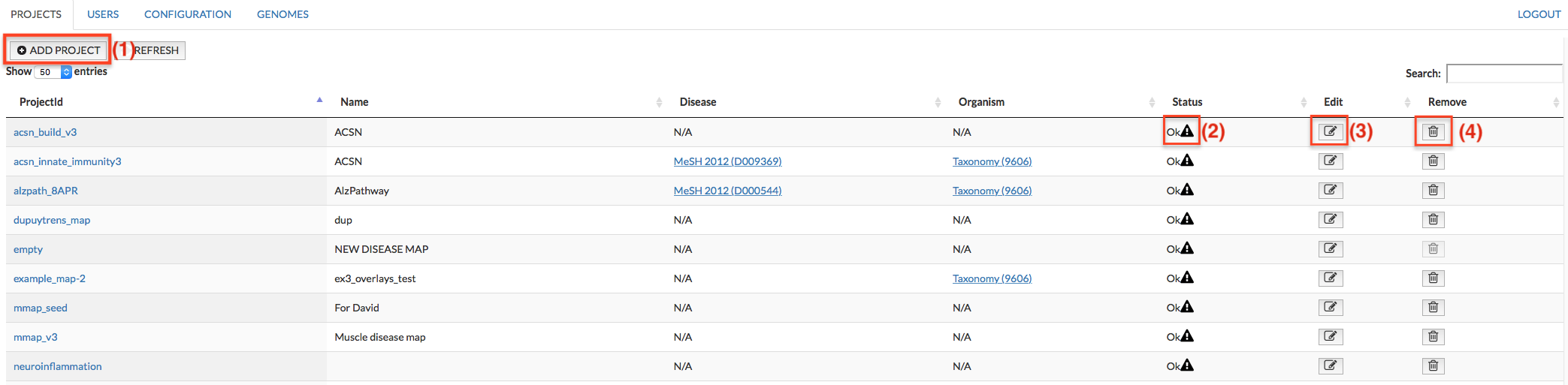
PROJECTS#
This panel allows you to add new projects and manage existing ones. The panel allows you to (1) add new projects (2) examine messages generated during the upload of the project (3) edit them and (4) remove project.
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
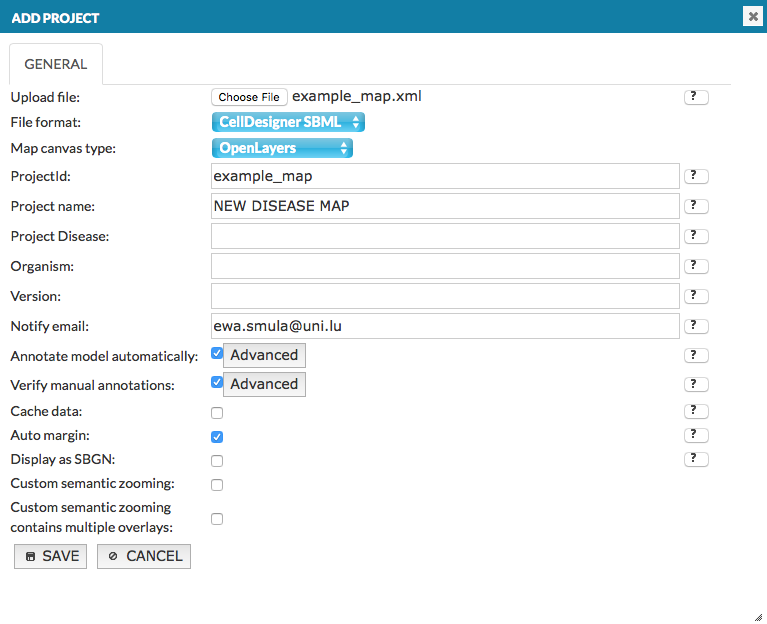
Add project#
The Add project button invokes a menu allowing you to upload your project and start its generation in the MINERVA platform.
 {:width=“800px”}
{:width=“800px”}
General - fields of the Add project window#
Upload file: Choose File invokes a file upload dialog. Available options and configurations of the source file are discussed in section Source file.
File format: Choose a format of uploading file: CellDesigner, SBGN or SBML
Map canvas type: Choose Google Maps API or OpenLayers to display the map, if you choose Google Maps Api you have to agree on Google Maps API Terms by ticking the checkbox.
ProjectId: a working name of the uploaded project on the MINERVA platform.
Project name: the name of the uploaded project displayed in the top left corner of the Administrator and User panels; your official name of the project.
Project Disease: the disease associated with the project, the code has to be a valid MeSH identifier, e.g.D010300. This is needed for chemical target search, see section User manual - chemical target.
Organism: the taxonomy id of the species, for which the map is primarily developed, e.g. 9606.
Version: a text field displayed next to the name of your project in the User panel.
Notify email: E-mail address that should be used for project change notifications.
Annotate model automatically: if this checkbox is checked, elements of the uploaded map will be automatically annotated using built in annotators. Behaviour of the annotators can be configured by clicking the Advanced button (see section Configure automatic annotation).
Verify manual annotations: if this checkbox is checked, elements and interactions of the uploaded map will be scanned for existing annotations; if present these existing annotations will be validated against a set of rules. Verification rules can be configured by clicking the Advanced button (see section Configure automatic verification).
Cache data: if this checkbox is checked, all hyperlinks in the project resolved by MIRIAM repository (e.g. cross-links to external bioinformatics databases) are resolved and cached.
Auto margin: if this checkbox is checked, upon generation of the graphics, empty spaces surrounding elements and interactions will be cropped.
Display as SBGN: if this checkbox is checked, the uploaded model will be displayed in SBGN format, instead of default CellDesigner format.
Custom semantic zooming (CSZ): if this checkbox is checked, semantic zoom defined by user in the upload file is displayed. The details about CSZ in User manual - content curation.
Custom semantic zooming contains multiple overlays: works only if (above) CSZ checkbox is ticked. Check the checkbox to display each custom semantic zoom level as overlay in the General Overlays panel in the map
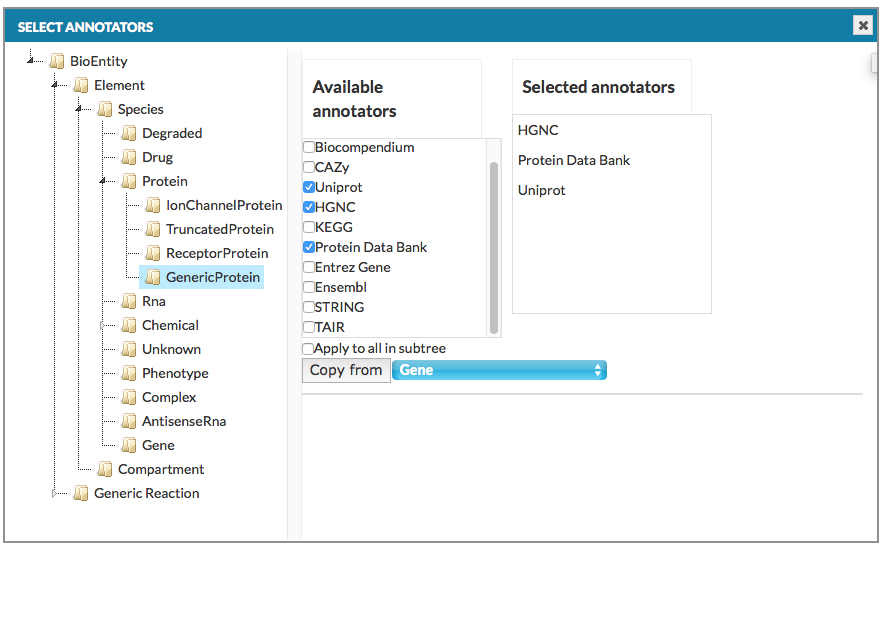
Configure automatic annotation#
The Advanced button, next to the Annotate model automatically checkbox under Add project button, invokes a dedicated configuration window (see below).
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
Clicking on each element type from the tree in the left panel, an annotator can be assigned in the right panel that will attempt to automatically retrieve information from external bioinformatics databases for each relevant element and annotate them. Copy from button in the right panel copies annotators set from other objects we choose (see above image: GenericProtein will get the same annotators as Gene already has set). Important note: Settings for lower hierarchy levels are overridden by settings for upper hierarchy levels. For instance, if no Ensembl annotation is selected for GenericProtein, but Protein selects Ensembl, GenericProtein will be automatically annotated with Ensembl either.
There are a number annotators available, utilizing either the name, or existing identifier of an object:
- BRENDA
-
- BRENDA identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the BRENDA ontology tree
- CAZy
-
- CAZy identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the CAZy ontology tree
- ChEBI
-
- ChEBI identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the ChEBI ontology tree
- ENSEMBL
-
- ENSEMBL identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including symbol, full name, synonyms, HGNC symbol and identifier, and Entrez Gene identifier
- Entrez Gene
-
- Entrez Gene identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including full name, synonyms, description, HGNC symbol and identifier, and ENSEMBL identifier
- Gene Ontology
-
- Gene Ontology identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including full GO definition for this identifier
- HGNC
-
- HGNC identifier, if present, or, if absent, name of an element will be used to retrieve additional information, including full name, symbols, description and RefSeq identifier, ENSEMBL identifier, Entrez Gene identifier
- KEGG
-
- KEGG identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the KEGG ontology tree
- Protein Data Bank
-
- Protein Data Bank identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the Protein Data Bank ontology tree
- STRING
-
- STRING identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the STRING ontology tree
- TAIR
-
- TAIR identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including synonyms, parents and children in the TAIR ontology tree
- UniProt
-
- UniProt identifier, if present, will be used to retrieve additional information, including HGNC symbol and identifier, and Entrez Gene identifier
- Biocompendium
-
Warning! this annotation service is unstable due to maintenance
- Name of an element will be used to retrieve additional information, including: full name, symbols, description and identifiers: RefSeq, ENSEMBL, Entrez Gene identifier, HGNC symbol, KEGG, Reactome, PubMed and others
Configure automatic verification#
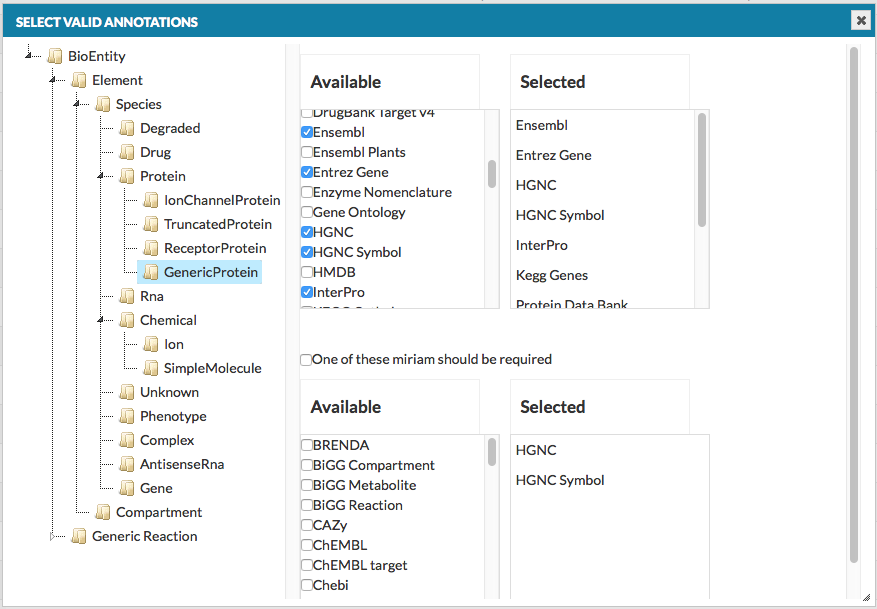
The Advanced button, next to the Verify manual annotations checkbox under Add project button, invokes a dedicated configuration window (see below).
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
-
- top right panels
- A list of MIRIAM identifiers which are considered valid. All elements or interactions in the uploaded model, annotated with an identifier outside of the valid list will be flagged as warnings.
-
- bottom right panels
- A list of mandatory MIRIAM identifiers can be assigned. If checkbox One of these miriam should be required is checked, all elements or interactions in the uploaded model, annotated without at least one identifier marked as required list will be flagged as warnings.
Save button: project generation#
Clicking Save button at the bottom of the Add project dialog window will start generation of the project. The window will refresh automatically, showing status changes during the process. Also, you can refresh it manually using Refresh button in top left corner. Any warnings raised during the process will cause an exclamation mark icon to appear next to the project status. The list of warnings is extended gradually, and you need to wait for the project completion to see the full list. You will receive an email notification after the generation is complete.
It may happen that the project generation will result in a failure. An icon will be displayed, and mouse over it will display the reason for failure. Moreover, you will receive an email message detailing the error you have received.
Status - examine warnings#
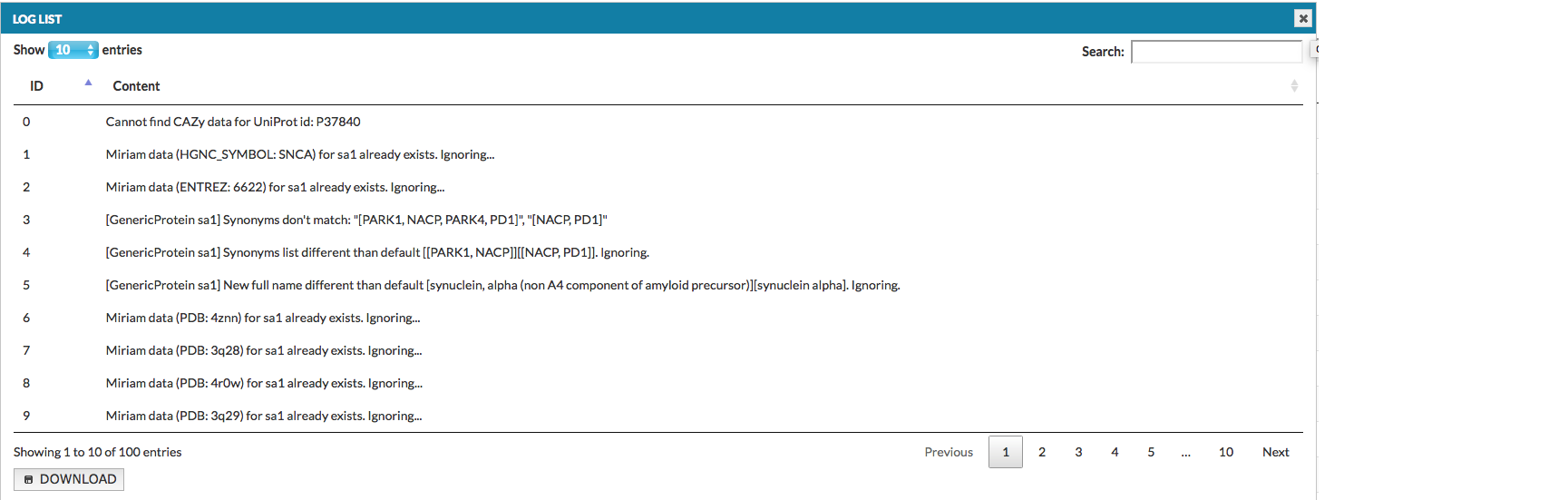
Clicking on the exclamation mark icon (if present) next to the project status description, will display the list of warnings raised during the generation of this project (see below).
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
The list can also be downloaded as a tab-delimited text file. Types and identifiers of the elements and interactions are listed on the left side of column Content, while the nature of an error is provided on the right. The table below lists possible errors and their explanations:
| Warning type | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Warnings generated by automatic annotation | |
| [Annotator] annotation problem | [Annotator] (e.g. HGNC) could not retrieve correct information for this element or interaction. The probable reason is wrong manual annotation, or name, of this element or interaction |
| Cannot find information for element. | None of the assigned annotators were able to retrieve information for this element or interaction. The probable reason is wrong manual annotation, or name, of this element or interaction |
| Chemical name cannot be found in ChEBI: [name] | ChEBI annotator could not annotate the element or interaction correctly by name, as [name] is not a ChEBI-recognized name. The annotation by manually provided identifier may still be successful. |
| Former symbols list different than default [list]. Ignoring | Existing annotation of an element (list of symbols) is different than the [list] retrieved by one of the assigned annotators. |
| New full name different than default [full name]. Ignoring. | Existing annotation of an element (full name) is different than the [full name] retrieved by one of the assigned annotators. |
| New symbol different than default [symbol]. Ignoring. | Existing annotation of an element (symbol) is different than the [symbol] retrieved by one of the assigned annotators. |
| Synonyms list different than default [list]. Ignoring. | Existing annotation of an element (list of synonyms) is different than the [list] retrieved by one of the assigned annotators. |
| Warnings generated by verification of manual annotation | |
| contains invalid annotations:[annotation] | Configuration in Validate manual annotations did not foresee [annotation] as allowed for this element or interaction. |
| misses one of the following annotations:[list]. | Configuration in Validate manual annotations required one of [list] of annotations for this element or interaction, but none was found. |
| misses annotations. | No annotation exists for this element or interaction. |
| Unknown miriam uri: [MIRIAM type] | An element or interaction was annotated with [MIRIAM type] - this type of identifier is currently not handled. |
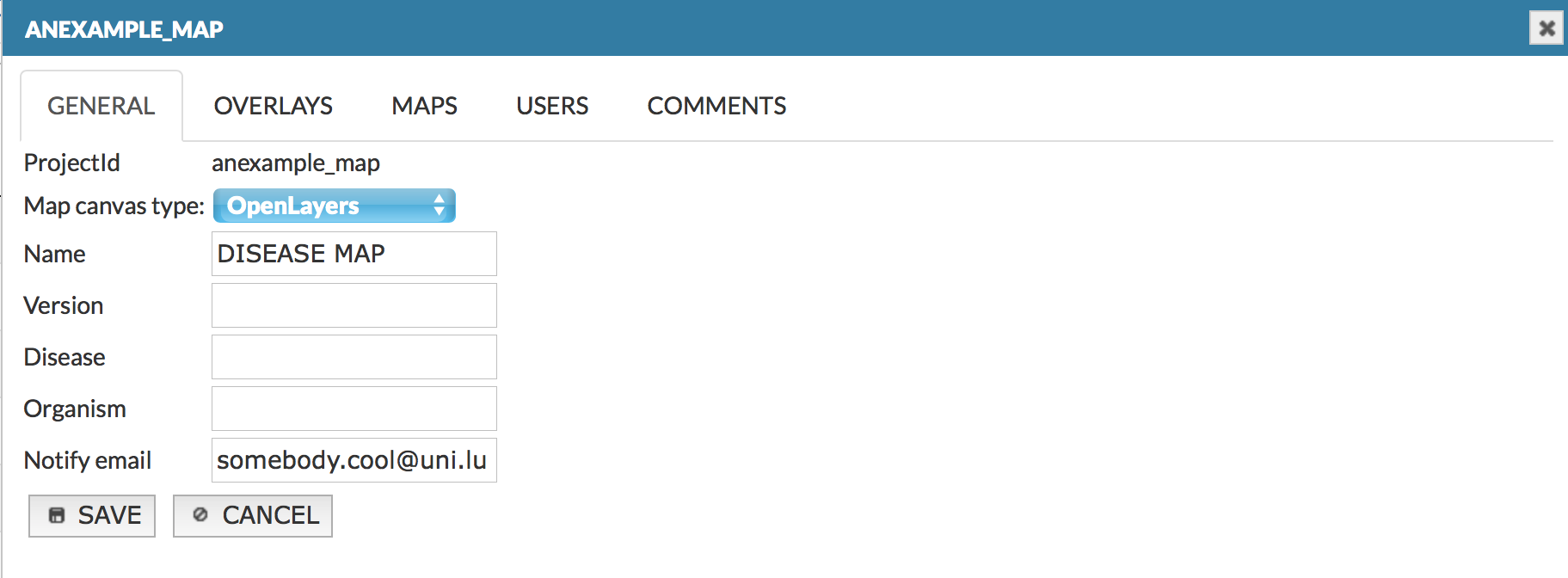
Edit project - general#
This panel allows you to manage on (see image below):
- General edit information about this project: canvas type, name, version, disease and organism type or notify email address
- Overlays manage overlays for this map, both general and user-provided
- Maps manage the main map and submaps either
- Users allows to manage users’ rights to access and manage this map
- Comments manage comments provided by users of your maps
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
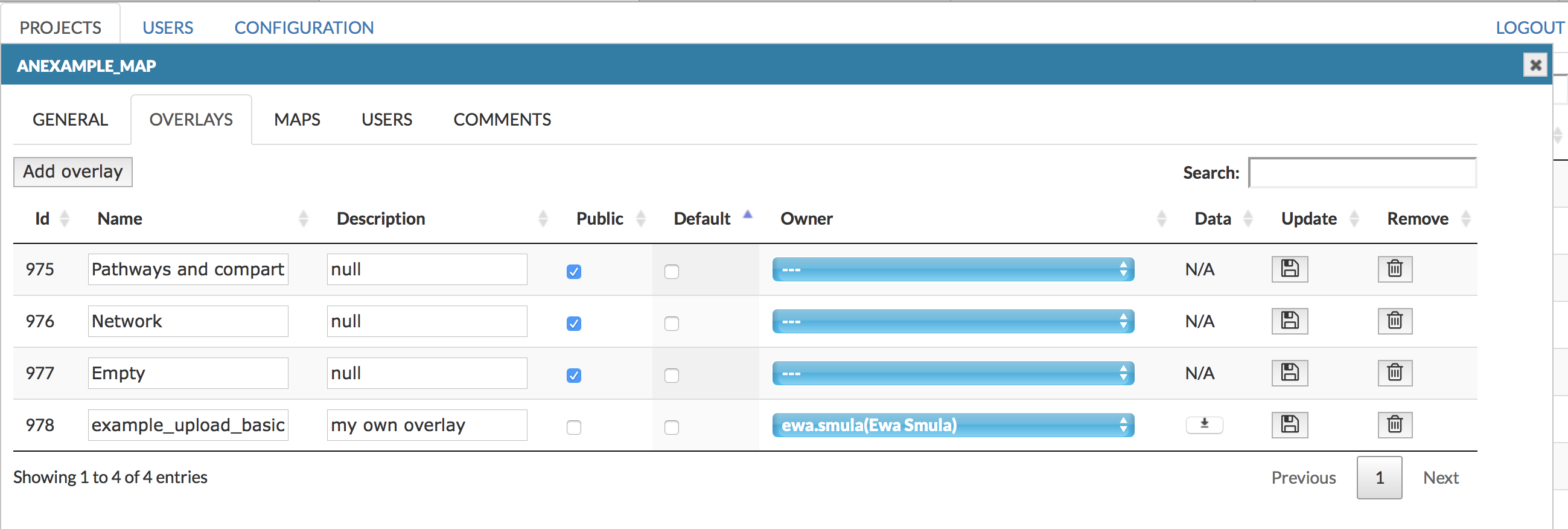
Overlays#
This tab allows you to add new overlay and edit the details about the overlays and their ownership. You see here overlays that have been:
- uploaded with the project, if it contains overlays already (see sections Add project and Source file) Important! Overlays named Pathways and compartments, Network and Empty allow for different ways of displaying the map’s content, and they don’t have any data associated with them.
- uploaded by the users (see section User’s manual - Upload user-provided overlay data)
- uploaded by the administrators by Add overlay button in top left corner
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
In this tab, besides Name and Description, the following columns are available:
- Public - Overlay is available to any user
- Default - this checkbox sets the default view of the map
- Owner - the user having the access right to a given overlay. Dropdown menu allows to choose from existing users. Important! Choosing the owner to be ‘N/A’ (top of the list) makes this overlay a General overlay, publicly visible for all users
- Data - action buttons allowing to download the associated dataset of a particular overlay
- Update - action buttons to save any changes in the configuration of a particular overlay
- Remove - action buttons to remove a particular overlay
Maps#
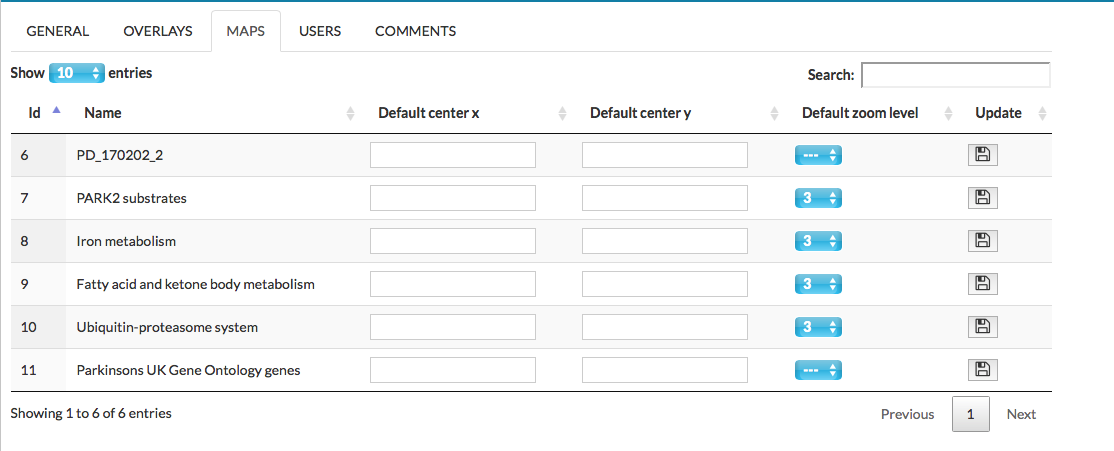
There is a list o all available maps (the main map and submaps) in the project, where you can change default displaying options of the maps, see below.
 {:width=“900px”}
In this tab the following columns are available:
{:width=“900px”}
In this tab the following columns are available:
- Default center x set the default center point of the submap/map
- Default center y set the default center point of the submap/map
- Default zoom level set the zoom level of the displaying map
- Update to save the changes
Users#
This tab contains a table of all users of the system (including the administrators) and allows to assign them rights to this particular map. It contains the following columns of checkboxes:
- Manage comments
- Manage overlays
- View project
- Update button, to save changes Ticking a checkbox in a respective column for a given user assigns this privilege to them. Each change needs to be saved with the Update privileges button.
General users privileges are discussed in detail in the following section USERS.
Comments#
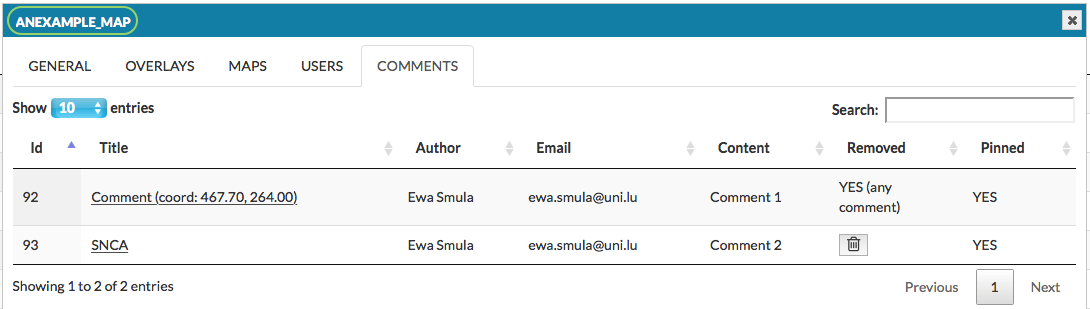
This panel allows you to manage comments provided by users to the particular map (see section User manual - Comments).
The field Title is a hyperlink to a given comment in the map. In the following columns there are author of the comment, his email and the content. Pinned informs if the comment’s icon is visible on the map. Users logged in as administrators have a possibility to delete a comment by pressing press the Remove button. The removed comment will no longer be visible among the pinned comments on the map, and its status will be updated in the Removed panel with comment in the brackets (see image below).
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
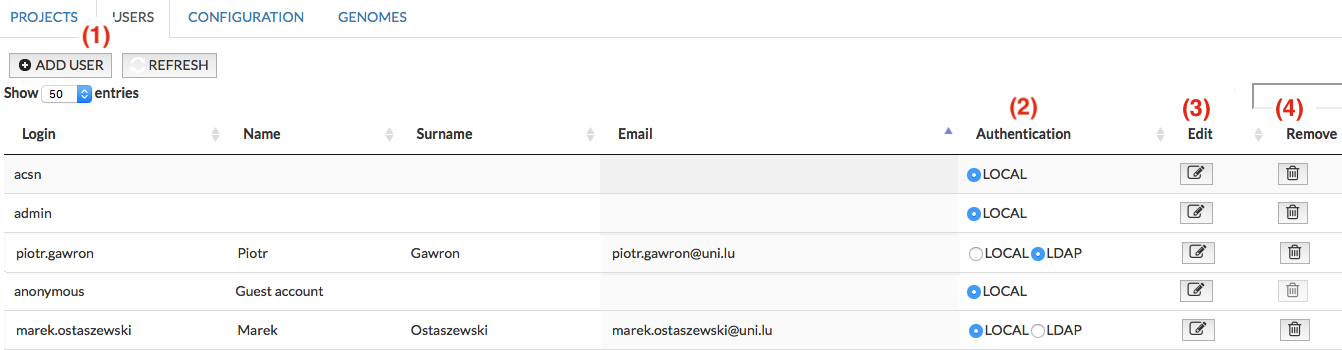
General USERS#
This panel allows you to Add (1), Edit (3) and Remove(4) users registered for a given instance of MINERVA platform. (2) allows to choose LDAP user authentication, see image below:
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
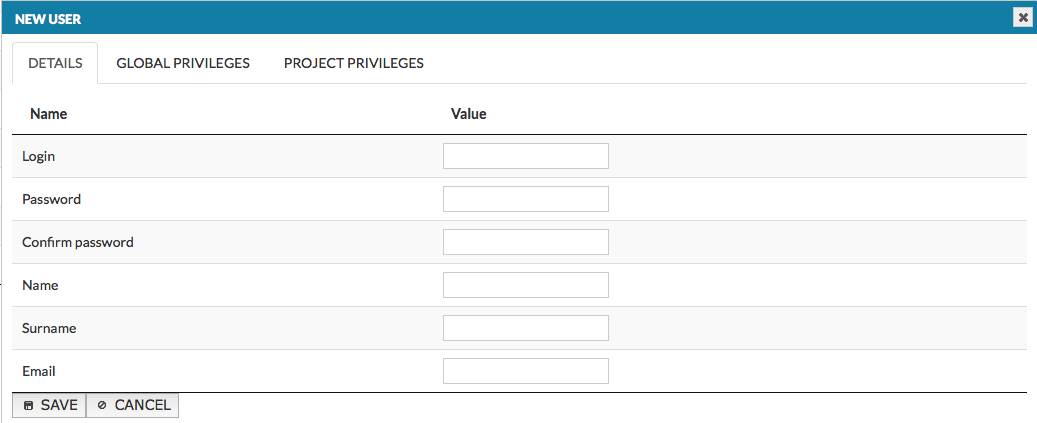
Registered users have access to additional functionalities besides accessing the visual content generated by the platform. Clicking on the Add user button invokes the window (see below) allowing to set login, password and personal details of a new user. The two next tabs in the window allow to set global privileges and project privileges of the new user. The panel to Edit already existing user is identical as the Add user window, with the exception that the login is assigned and not editable. Remove button removes this registered user from your instance of MINERVA platform.
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
Manage of user’s privileges:
- Global privileges concern all projects on your MINERVA instance
- Add project checkbox, if checked, grants the user access right to the Add project button and permits the user to add new projects
- Custom overlays field defines how many overlays can be created by a given user across all projects they have access to on your instance of MINERVA platform
- Manage configuration checkbox, if checked, grants the user access right to access Configuration tab and permits them to manage the global configuration of your instance of MINERVA platform.
- Manage genomes checkbox, under development - do not change the default setting.
- Map management checkbox, if checked, grants the user right to access Map manager tab and manage existing projects
- User management checkbox, if checked, grants the user right to access the User manager tab and permits the user to manage users on your instance of MINERVA platform.
- Project-specific privileges concern only the project, for which they are configured
- On the top: Default privilege for a new project checkboxes - set up default user’s privileges for any new project
- The list of available projects on your MINERVA instance, contains four columns:
- ProjectId name of the project
- Manage comments checkbox, if checked, grants the user right to the comments tab in Edit project and allows them to manage comments for this specific project
- Manage overlays checkbox, if checked, grants the user right to manage overlays of all users for this specific project
- View project checkbox, if checked, grants the user right to view this specific project Important for non-administrator users only this box should be selected.
CONFIGURATION#
Configuration tab provides a summary of the current version of your MINERVA instance. Moreover, it allows privileged users to configure global parameters of the MINERVA instance. You can choose a particular category from context menu, see image below, or leave the context list blank and see all options at once.
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
Global MINERVA configuration category are:
Email notification details
- E-mail address: e-mail address used for sending notifications about the activity of your MINERVA instance - project uploads, comments, etc.
- Email content used for requesting an account
- Email used for requesting an account: the Login tab in the user interface features a Request for an account button; clicking the button will auto-generate an message (with content as per above Email content used for requesting an account) to the e-mail, or list of e-mails separated by a semicolon, provided in this field
- E-mail server login, E-mail server password, IMAP server, SMTP port and SMTP server: configuration of your mail server for notification sending
Server configuration
- Default project id: the project that will be displayed by default under the root address of the platform (your.url/MapViewer/)
- Domain allowed to connect via x-frame technology: the address of a website allowed to embed this instance of MINERVA via x-frame technology
- Google Analytics tracking ID used for statistics: MINERVA platform offers integration with Google Analytics to track user activity of your MINERVA instance by providing an appropriate Google Analytics ID in this field
- Path to store big files: location in the directory structure of this MINERVA instance to store big files
Legend and logo
- Legend 1-4 image file: location in the directory structure of this MINERVA instance for displayed legend images
- Logo description: the popup text that will be displayed upon mouse over your logo
- Logo icon: the filename of your logo icon, displayed in the bottom-left corner of the visualized content
- Logo link (after click): the website to which you will be redirected after clicking on the logo
- Show reaction type when browsing map checkbox
- URL of platform Terms of Use file
- User manual file: location in the directory structure of this MINERVA instance for the user manual file
Point and click
- Max distance for clicking on element (px): the content visualized by MINERVA platform is interactive, and clicked elements or interactions are recognized by the vicinity of the click event. This parameter controls, how close to an element or interaction, in pixels, you need to click to select them
- Max number of results - this value indicates the max number of elements that will be returned from search, not the number of aggregated elements in the search box
Overlays
- Opacity used when drawing data overlays (value between 0.0-1.0)
- Overlay color for negative/positive values: configuration of overlay display - what colors should be used for positive and negative values. Values close to zero have the lowest color saturation, values close to -1/1 have the highest color saturation (see section User manual - Upload user-provided overlay data)
- Overlay color for value=0
- Overlay color when no values are defined: configuration of overlay display - what color to use for coloring named elements (see section User manual - Upload user-provided overlay data)
Default user privileges Default user privilege for manage comments, overlays and view project checkboxes - tick it to set up default user’s privileges for any project.
LDAP configuration
- LDAP address - address of the machine where LDAP server is located
- LDAP port - port on which LDAP is listening (by default it’s 389, for SSL connections usually it’s 636)
- LDAP uses SSL - checkbox, should we use SSL for LDAP connection
- LDAP bind DN - Distinguished Name of the user account that should be used for LDAP connection (this user should be able to search/list accounts on LDAP server)
- LDAP password - password for the LDAP bind DN
- LDAP base DN - definition of the point from where a server will search for users
- LDAP filter objectClass - this parameter allows to filter by objectClass type of LDAP entry; * value skips the filtering
- LDAP first name attribute - which attribute in LDAP directory corresponds to “First name” of the user
- LDAP last name attribute - which attribute in LDAP directory corresponds to “Last name” of the user
- LDAP email attribute - which attribute in LDAP directory corresponds to the user email address
- LDAP filter - when there are many accounts in LDAP administrators create groups of users that have access to specific systems, this filter allows to define LDAP filter that will limit set of accounts that can access minerva, empty string disable filtering
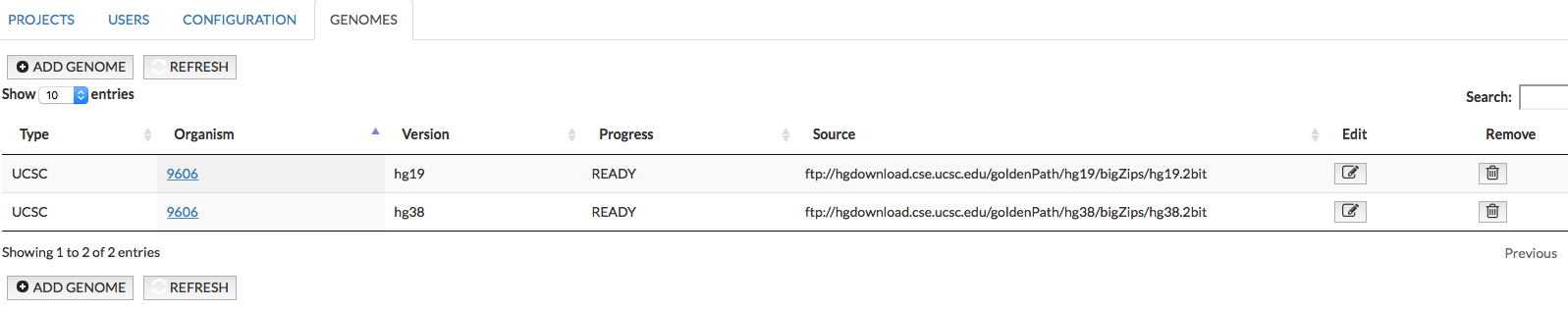
GENOMES#
In the section Genomes administrator can provide a reference genome to support displaying the genetic variant overlays and genome browser in the map. Currently MINERVA supports human genomes data from UCSC Genomics Institute. In the image below, see the fields:
- Type informs about type of data, currently Minerva supports genome data from UCSC
- Organism identifier of the organism, for which this reference genome is added (e.g. 9606)
- Version of the genome the organism, for which this reference genome is added (e.g. hg19)
- Progress - the percentage value of the upload progress of the new genome
- Source - url address of the genome data; sets up automatically after selecting Version, or user can paste own url address. Note: the file must be in .2bit format.
- Edit/Remove buttons allows to edit the gene mapping and remove the genome from the instance
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
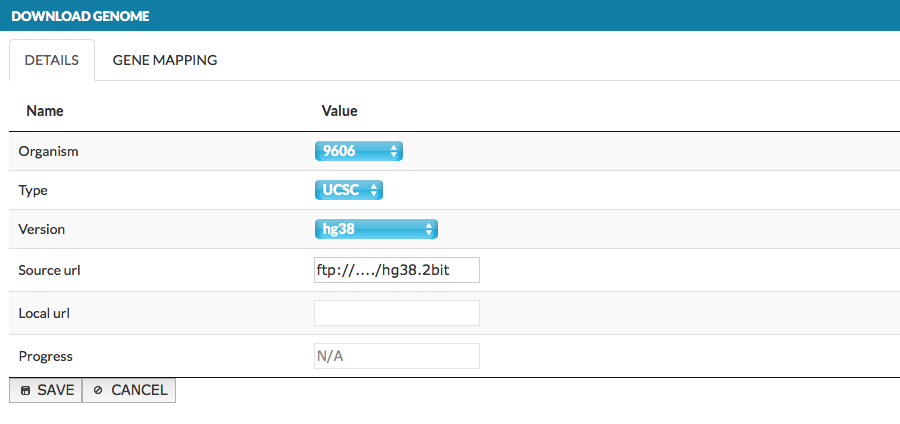
Add new genomes#
In top left corner choose ADD GENOME button; the window pops up, as shown below:
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
The window contains two tabs:
- DETAILS - select new genome parameters as described above
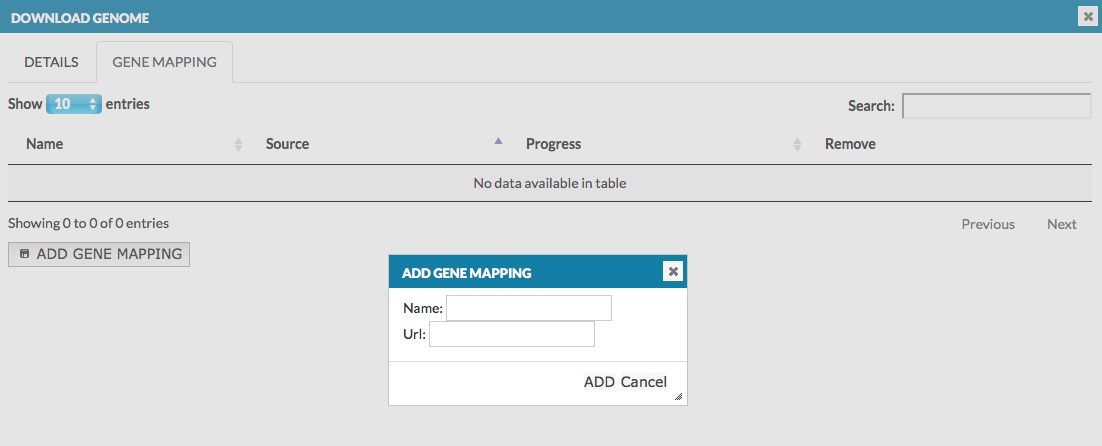
- GENE MAPPING - allows to provide information about the gene loci in the genome, which are visualized on the blue axis in the genome browser. In the dialog window, put the name of the data set and its url address. The name will be also displayed in the genome browser (in this manual it is called gene ref), see User manual - Overlays. The data must be provided in .bb format file. More details how to create .bb file.
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
Source file#
The source file is uploaded to establish a project on your MINERVA instance. The source file can be SBGN-compliant file or SBML file (both are basic upload) or advanced upload using archived file.
SBGN-compliant file#
If it is a SBGN-compliant file in the .xml format, a single SBGN file is uploaded via the Add project button (it is shown in section Add project). This way the SBGN-compliant network is uploaded, without additional files (basic upload).
SBML file#
SBML format is supported by MINERVA. Certain modifications of SBML file are essential before upload:
- Elements and reactions should be defined by SBOTerms, if not, all elements are shown as small molecules and all reactions are displayed as state transitions; see the list of CellDesigner types matching SBOTerms
- Displaying Miriam annotations requires additional xml blocks, similar to CellDesigner RDF annotation.
- If SBML file contains xml block layout (describing position of elements and reactions) MINERVA supports it and displays map according to it
Known issues#
- Block annotation inside block model causes problems with the upload, delete the whole block to fix the upload, the issue will be solved in the following MINERVA release
- Block kineticLaw in SBML file may crash upload of the map. This will be indicated in the project status; deleting the particular kineticLaw block will fix the upload with no loss of map displaying quality. The issue will be solved in the following MINERVA release, as MINERVA aims to support kinetics of reactions
Find out how to amend an SBML file in Example 02 - SBML file modifications.
Archived file (advanced upload)#
Advanced upload mode assumes that a zip-compressed directory will be submitted as an input, with the following structure:
- main map: file in a SBGN-compliant format (CellDesigner, pure SBGN or SBML)
- images: directory with files (see Appendix Images)
- layouts: directory with overlay files (see Appendix Overlays)
- submaps: directory with submap files (see Appendix Submaps)
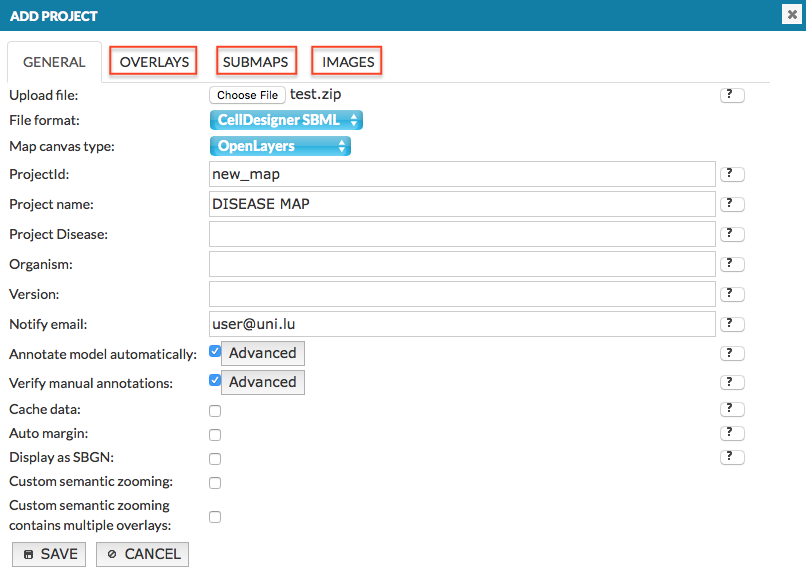
After upload, in Add project window additional tabs become available. Each tab represents subfolder of a source file, see below:
 {:width=“900px”}
For an example, see Example 04 - The advanced file upload.
{:width=“900px”}
For an example, see Example 04 - The advanced file upload.
Appendix#
Detailed description of each section of the source file follows below:
Overlays#
The layouts subdirectory contains files with custom coloring of the uploaded content that will be accessible to all the users. The format is identical to the format of files uploaded by registered users. See Section Upload custom data - format for details on file format.
Submaps and mapping file#
The submaps subdirectory contains SBGN files that will be displayed in the Submaps tab in the functional area of the User view (see section User view - Submaps tab). Additionally to the submaps files, one additional file, a submap mapping file, can be added to the directory. This file describes connections between the submaps and the main map itself.
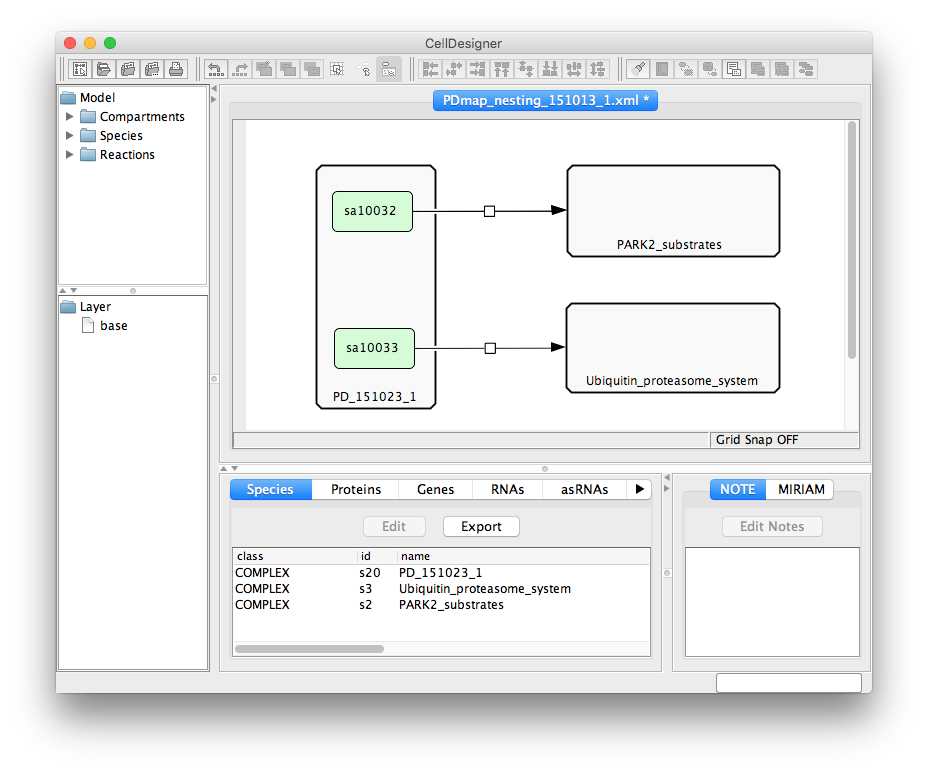
Submap mapping file is a CellDesigner file, in which relations between the uploaded maps are represented graphically. Two types of components and one type of interaction is considered when parsing this file:
- Complex should be named as a map file (the main map, or a submap), but without the .xml extension
- Protein should be named as an alias of referred element in the source file (the main map, or a submap). Please note that a species alias is not the same as a species identifier! (see remark below)
- State transition reaction describes relations between components of the map.
Remark to alias vs identifier: CellDesigner has a single species identifier for all copies of a certain element (e.g. protein) in a file. Different instances of the same element have a distinct species alias. It is the species alias that is used to link specific map elements with submaps.
A screenshot below demonstrates an exemplary submap mapping file.
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
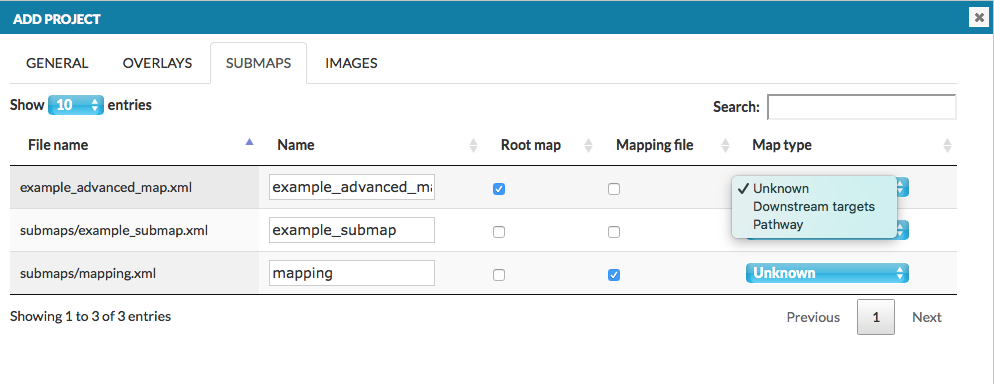
Section Add project -> Submaps describes how main map and uploaded submaps are related, see image below:
- Filename: name of one of multiple files
- Name: name of the main map, or a submap, in the project
- Root map: a column of checkboxes; only one position must be checked, corresponding to the main map in the project
- Mapping file: a column of checkboxes; only one position must be checked, corresponding to the mapping file describing relationships between the main map and the submap(s)
- Map type: choose if the submap is a pathway or a list of downstream targets, or leave unknown
 {:width=“900px”}
{:width=“900px”}
Images#
The images subdirectory contains static image files in .png format that will be displayed after pressing the Show overview button (see User manual - Show overview). Besides the images, the directory also has to contain a text, tab-separated file named coords.txt, describing links between the images and the associated network(s). The coords.txt file is a table with the following structure:
- FILE - linked image file
- POLYGON - a sequence of points in the linked image file forming a polygon, which will be treated as an active area for the link. The points should be
x,ypairs separated by a spacebar, representing absolute coordinates of the pixels in the corresponding image. They should be provided in a single line - LINK_TYPE - the type of link to the image, has to be one of the types specified below; link type determines the usage of the remaining fields.
- IMAGE - links to another image of the uploaded set
- MODEL - link to the main map, or one of the submaps
- SEARCH - link to the results of a search query
- LINK_TARGET - determined by the field
LINK_TYPE- if IMAGE - filename, must be one of the uploaded image files in the images directory
- if MODEL - filename of the uploaded main map, or one of the submaps
- if SEARCH - query to be executed and linked (see Section User manual - Search)
- MODEL_COORDINATES - if the field
LINK_TYPEisMODEL, this field should contain absolute coordinates of the point in the target map, in the formatx,y; otherwise it should be left empty - MODEL_ZOOM_LEVEL - if the field
LINK_TYPEisMODELand absolute coordinates are given, this field should contain a number corresponding to the zoom levels in the display area; otherwise it should be left empty. The the furthest zoom out has number 1, each zoom in increases the zoom number by one. Smaller maps will have less zoom levels than big ones. Try uploading the map without images first, and assess the coordinates and zoom levels for the version with images - COMMENT - a field for supplementary information, not used for configuration.
Example of a coords.txt file:
| FILE | POLYGON | LINK_TYPE | LINK_TARGET | MODEL_COORDINATES | MODEL_ZOOM_LEVEL | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| image.A.png | 51,218 107,218 107,252 51,252 | MODEL | PD_151023_1.xml | 7488,11986 | 4 | A link from image.A file to a point in the display area with zoom level 4 |
| image.B.png | 15,187 73,187 73,52 15,52 | IMAGE | image.A.png | A link from image.B file to invoke image.A | ||
| image.C.png | 30,8 10,8 10,7 30,7 | SEARCH | reaction:c1,reaction:c2 | A link from image.C to results of a search query pointing to interactions c1 and c2 |